MIB Explorer Pro can be used as a monitoring server that collects, aggregates, and otherwise computes data from remote SNMP entities. The collected data can then be stored on disk in MIB Explorer‘s native format or XML.
Existing monitor (configuration) files can easily migrated to a database using the -m2db parameter of MIB Explorer Server (mxp-server).
In addition, with version 3 or later, monitoring data can also be stored using Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) database connections to DB servers. Currently IBM® DB2® 9.7 or later1 and PostgreSQL are supported out-of-the-box. See “Monitors (Pro Edition)” on page 111.
For presenting the monitoring data to end-users, MIB Explorer Pro also provides a HTTP-Server which can be configured and instrumented using MIB Explorer scripts. See also “Scripts (Pro Edition)” on page 90.
All the above mentioned server features are available in the GUI application of MIB Explorer Pro which is started by default. For pure server use, a headless (non-GUI) application can be the better choice - especially if the server should run in a command line oriented environment. Therefore, MIB Explorer Pro can be run headless too while monitoring, HTTP server, and scripts are configured at server start. Running monitoring scripts can be reconfigured at runtime too.
The following sections describe the server related functions of MIB Explorer Pro.
16.1MIB Explorer Headless Server
When MIB Explorer is run without command line arguments it starts with its graphical user interface (GUI). This is the best choice for most use cases. However, there are use cases where running MIB Explorer without a GUI is more appropriate, for example:
to run monitors as background process to create chart images for a Web server
to run scripts to automate SNMP configuration, test agent implementations, or send traps.
To run a monitor or script in server mode:
1.Change the working directory to the MIB Explorer installation directory.
2.On UNIX systems use the mxp-server.sh script instead mxp-pro.sh. This script starts the JRE with the "-Djava.awt.headless=true" option set, so that MIB Explorer can even be run in server mode on UNIX systems without X installed:
mxp-server.sh {options}
On windows systems, start the Java virtual machine by using:
mxp-server.bat {options}
Without special script from any operating system command line with Java installed:
java -D java.awt.headless=true-jar mxp_pro.jar -server {options}
where in all cases {options} is replaced by any combination of the below listed options.
The table below shows the available options for the headless MIB Explorer version. All options can be specified more than once, although in case of -h and -w only their last occurence will be effective then.
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
-? |
Print usage information on the console. |
|
-a[ccept] secret |
Accept client connections from MIB Explorers that use the specified secret (see “Server” on page 16). This option can be supplied more than once. By default only the secret specified for this MIB Explorer user/configuration will be accepted. |
|
-acceptall |
Disable client authorization. All MIB Explorer clients will be able to connect as long as the "server.security" policy allows it (see option -securitymanager below). |
|
-d[isableMonitorScripting] |
Disable scripting for monitors run by the server. Because a monitor script can execute system commands and send emails, using this option provides another level of security, if necessary. |
|
-http-port port |
Specify the port for the built-in HTTP server (this option has no effect if the HTTP server is disabled by the option "http-servlets off". |
|
-http-serlvets off|all|monitorcharts| |
Disable the built-in HTTP server by setting this option off. Enable all servlets by using all or enable any servlet subset by specifying the monitorcharts, monitordata, and script options once for each servlet to enable. |
|
-h[eight] |
Set the default height of monitor charts in pixels, default is 480. This size is used if a monitor's preferred height is 0 and the height is not specified otherwise (for example by providing the height parameter for the HTTP monitor servlet). |
|
-w[idth] |
Set the default widths of monitor charts in pixels, default is 640. This size is used if a monitor's preferred width is 0 and the width is not specified otherwise (for example by providing the width parameter for the HTTP monitor servlet). |
|
-m2db jdbc-url driver-class |
Migrate all for restart configured monitors and all monitors specified using the -m option to a database monitor on the relational database accessible through JDBC using the URL jdbc-url. For PostgreSQL the URL has the format: jdbc:postgresql://hostname:port?user=username&password=password The URL format for DB2 is (the trailing ; is important!): jdbc:postgresql://hostname:port:user=username;password=password; The driver-class name identifies the DB version and driver to be used. For PostgreSQL the driver class name is org.postgresql.Driver whereas for DB2 it is com.ibm.db2.jcc.DB2Driver. During migration, .xml and .mon files will be saved to the specified database and the access parameters will be stored for further reference in a file with .dbm extension in the same directory as the source file. Then the monitors are started and any collected data will be stored to the database only. If you want to rerun the monitors from the database after migration, you will have to specify the saved files on startup with the -m option and/or replace the monitor paths in the mxp4.cf file in your home directory with the migrated ones ending with .dbm. |
|
-m[onitor] filename |
Run the specified monitor file. The file specified by filename will be rewritten (updated) after each refresh*. Any changes made to the monitor by a MIB Explorer GUI while this server is running will get lost then. |
|
-server |
Start MIB Explorer Pro as MIB Explorer Server (without GUI). |
|
-s[cript] script output |
Run the script script and write the output to the file output. |
|
-mibs[et] name |
Load the specified MIB set in addition to already loaded modules (i.e. those modules that were loaded when the MIB Explorer GUI has been exited last). |
|
-rmihost hostname |
Sets the java.rmi.server.hostname system property that is necessary to allow remote clients to connect to the MIB Explorer server. Client connections might be possible without setting this option, but that depends on your environment. |
|
-securitymanager |
Run the server with a security manager. This options requires specifying a policy file with By specifying this option, the connections allowed to and by the server, file access, and other security settings can be controlled via a policy file. An example policy file is located in the MIB Explorer installation directory. It can be edited by using a text editor or the policytool from the JDK bin directory. |
|
-p[ath] monitor-path |
Directory path that specifies where to load and store monitor files. If this option is not given, the last used directory when a monitor file had been saved by the MIB Explorer GUI will be used. |
|
-l[oglevel] category=level |
Set (override) the configured log level for category with level . Use, for example, 'Script=OFF' to switch off logging for scripting. |
|
*Only .mon and .xml files are rewritten. Database monitor configuration files with suffix .dbm are opened read-only. |
MIB Explorer Pro contains an internal HTTP server which is available for the MIB Explorer Pro GUI application and Server. The HTTP server can be configured by through the Preferences editor of the GUI application. Some basic settings can be overridden by command line options of the MIB Explorer Server.
Fields of application for the HTTP server include (besides others):
Make monitor charts and/or data available via HTTP.
Create your own simple Web application to monitor and/or control SNMP enabled devices through a Web interface.
Integrate monitor charts and/or data into your own Web application.
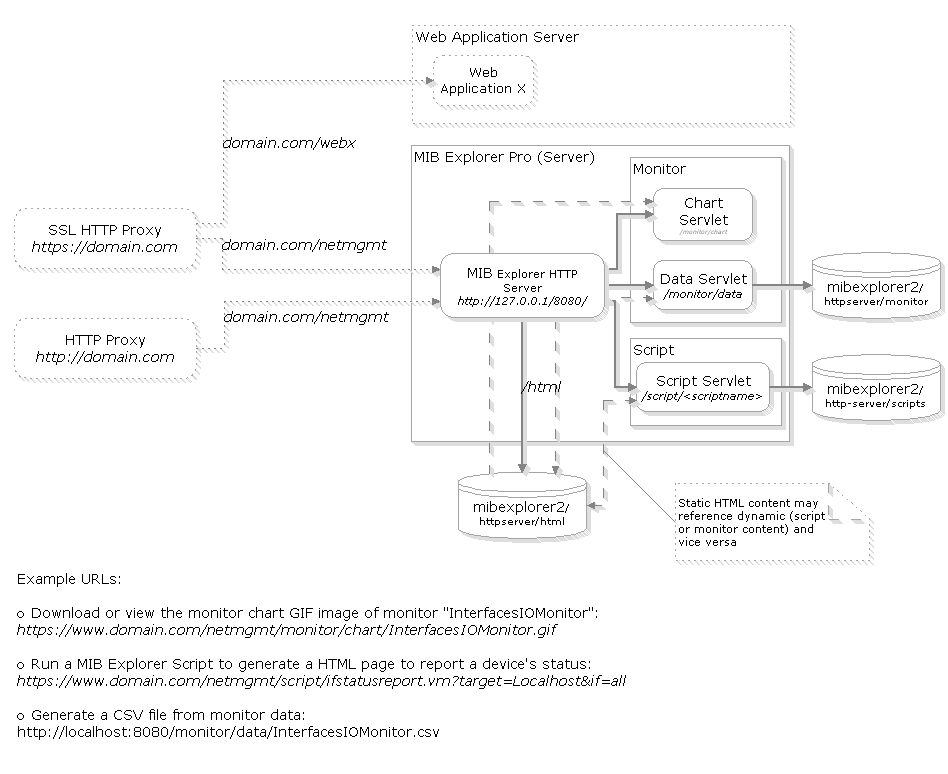
The figure below illustrates an example architecture that can be setup with MIB Explorer Pro's HTTP Server. The architecture suggests that MIB Explorer's HTTP server is run behind a HTTP reverse proxy server (could be SSL enabled or not). This is not a requirement, but this approach is recommended if
"access to the content provided through MIB Explorer's HTTP server needs to be secured or
"the content provided by MIB Explorer's HTTP server needs to be integrated into a Web application.
The default port for the HTTP server is 8080. You can change it in the HTTP server preferences to any other value - including the standard port 80 (on UNIX systems you will need system privileges to use that port).

|
16.2.2Customizing Dynamic Content
There are two ways to customize the dynamic content generation of the MIB Explorer HTTP server:
1.Provide a set of MIB Explorer Scripts to monitor and/or control SNMP enabled applications and devices. The context provided to the scripts is slightly extended compared to the available contexts for the Script tool. You can find the context reference in the section “Scripts (Pro Edition)” on page 90.
2.Provide your own monitor data servlet template that generates a HTML page or XML file from monitor data. The template monitor data servlet template is called with three contexts exclusively provided to the monitor data servlet and it is called with the utils context, well known from other script environments of MIB Explorer.
1. IBM and DB2 are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation, registered in many jurisdictions worldwide.