SNMP Management Information Base (MIB) specifications are documents containing definitions of management information so that network systems can be remotely monitored, configured, and controlled. MIB Explorer makes extensive use of all machine readable information within MIBs. This information is available as so called MIB modules.
MIB Explorer is a generic tool for managing any SNMP system. It has only very limited built-in knowledge of MIB information (see SNMPv3 User Administration). As a consequence, it is essential to MIB Explorer to be able to parse MIB modules and compile them into an internal format.
Once MIB module information is available, this Structure of Management Information (SMI) facilitate accessing, formatting, organizing, and modifying MIB object values.
The most important operations on MIBs are:
Getting MIB Modules.
Compiling MIBs.
Creating a MIB Repository.
Loading MIBs.
Deleting MIBs.
MIB specifications developed by the IETF working groups contain prose descriptions and references to other documents that enclose the actual MIB module(s). MIB Explorer compiles SMIv1 (RFC 1155) and SMIv2 (RFC 2578-2580) conforming MIB modules. However, MIB modules have to be extracted from RFC specifications before they can be compiled.
Whereas extracting MIB modules from RFC documents can be done manually by removing any prose descriptions, page headers, and footers from a RFC MIB text document, it is much easier to use the Tool Extracting SMI from RFC documents to create SMI MIB specification files that can be parsed by MIB Explorer.
If you are looking for an enterprise specific MIB module that did not came along with your SNMP device, then you might want to search for it on the Internet.
A MIB repository is a directory that MIB Explorer exclusively uses to store compiled MIB modules in an internal format. Before a MIB module can be loaded into MIB Explorer's MIB tree, it has to be compiled and stored into a MIB repository.
1.From the file menu choose Set MIB Repository. A File Open menu dialog box will appear.
2.Navigate through the file system to the directory where you want to create the MIB Repository.
3.Within that directory, create a new folder by clicking on the Create New Folder ( ) button. The new folder can be renamed by double-clicking it.
) button. The new folder can be renamed by double-clicking it.
Note: Do not double-click the new folder! Otherwise you cannot select the folder itself.
4.Choose the new (or any other empty folder) by selecting it. Click Open.
As long as a MIB Repository directory is used by MIB Explorer, it must not be altered outside MIB Explorer - except by other AGENTPP tools, like AgenPro or MIB Designer. Once a valid MIB Repository has been set, you may compile MIB files to store them in the repository.
1.From the file menu choose Set MIB Repository. A File Open menu dialog box will appear.
Note: Do not double-click the new folder! Otherwise you cannot select the folder itself.
2.Navigate through the file system and select the MIB Repository directory you want to use.
3.Click Open.
The MIB repository will be verified. If any inconsistent or corrupted MIB modules are found, a dialog will be displayed with instructions to repair the repository.
Before you can compile MIB modules into MIB Explorer's internal format, a MIB repository has to be created where the compiled MIBs are stored. During the first startup of MIB Explorer you will be asked to specify a MIB repository.
Precompiled MIBs
MIB Explorer comes with a set of precompiled SMIv2 MIBs which are located in the repository directory of the MIB Explorer installation. MIB Explorer uses that directory as its initial default repository.
To Compile MIBs
1.From the File menu, choose Compile MIBs (or  from the main tool bar). A file open dialog will appear.
from the main tool bar). A file open dialog will appear.
Alternatively you may also use the Compile New MIBs menu item to compile only MIBs that are newer than the existing or not available yet in the repository. With the MIB Compiler settings, you can fine-tune the behavior of the Compile New MIBs operation.
2.Choose a MIB file, ZIP file or a directory and click Open. If you choose a file, then that file will be compiled and all contained MIB modules (typically one) are stored into the MIB repository
If you choose a directory or a ZIP file, then recursively all contained files will be parsed. All successfully parsed MIBs will be automatically sorted by their dependencies and then compiled into the MIB repository. Directories may also contain ZIP files.
3.After compilation a message dialog with summary information is shown.
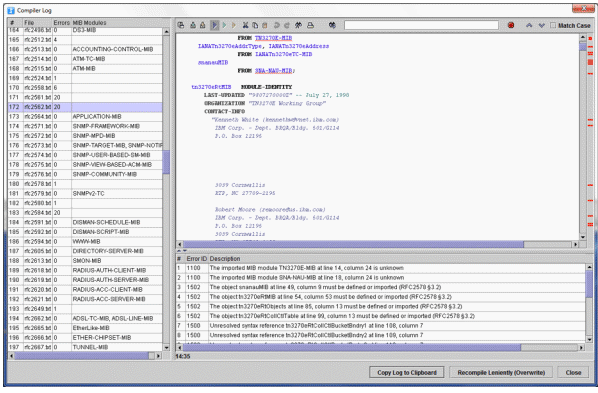
4.Press Details to open the Compiler Log window (see Figure 1). It lists status information for each MIB file compiled. A MIB file that failed to compile has more than zero errors Errors column. To view the errors detected for that file, click on that row. The right pane will then show the file‘s content and the list of errors below. By clicking on an error description, the error location text is selected in the editor.
5.The MIB modules of the successfully compiled MIB files are automatically stored in the MIB repository. From there, the MIB modules can be loaded into the MIB Explorer application.
Existing MIB modules will be overwritten (updated). If you do not want to change any MIB modules that already exist in the current MIB repository, then use Compile New MIBs from the File menu.
The Compiler Log dialog lists the status of all MIB files of a compilation run. If the compilation of a MIB file failed, the Status column displays the text Failed. The error messages for that file can be expanded by clicking on the + sign of the file's row. By selecting an error message, its description text will be displayed in the text pane on the bottom of the dialog.
The file name of the MIB file is displayed in the File column, whereas its complete path is displayed in the Path column.
To Correct a MIB File
Double click on the row corresponding to the MIB file you want to edit. The MIB file editor window will appear (see section MIB File Editor). Alternatively, you may double click on an error message to directly jump to that error location in the file.
If the error message selected includes location information about the error's line and column, then the editor's cursor will be placed at that location in the MIB file. When you have clicked on the file, the first error will be located. Otherwise, the first occurrence of the object name corresponding to a semantic error will be searched. The next occurrence of the object name may be found with the Find Again button  .
.
After having fixed the error, the MIB file can be saved and compiled again by using the Import button  .
.
Tip: You can print the expanded compiler log's content from the context menu.
If the compilation was successful, the editor window will be closed. Otherwise the cursor of the editor will be positioned on the new error.
MIB Explorer needs to load MIB modules from a MIB Repository into its memory to be able to display and use the contained information. For a better overview and performance, it is recommended to not load unneeded MIBs.
1.From the File menu, choose Open/Close MIB (or  from the main tool bar). A shuffle dialog will appear. It contains two lists of MIB modules. The left list shows all MIB modules currently not loaded but available from the MIB repository. The right list shows the MIB modules currently loaded.
from the main tool bar). A shuffle dialog will appear. It contains two lists of MIB modules. The left list shows all MIB modules currently not loaded but available from the MIB repository. The right list shows the MIB modules currently loaded.
2.Select any MIB modules you want to load from the left list of available MIB modules. Click on the Add button to move the selected modules to the right list of MIBs to be loaded. If a MIB that is moved to the right list depends on another MIB module that is currently not loaded, then that MIB (and all MIBs it depends on) will be also moved to the right list. This ensures that MIB Explorer has always a consistent view on MIB data.
3.Select any MIB modules you want to unload (close) from the right list. Click on the Remove button to move the selected modules to the left list of available MIBs. Loaded MIB modules that depend on the removed (unloaded) MIB modules will also be unloaded and thus moved to the left list.
4.Click on the OK button to execute the changes made. Depending on the number of MIB modules that need to be loaded, it may take a while until all modules are loaded and the MIB tree is refreshed.
Deleting a MIB module from a MIB Repository cannot be undone. A MIB module can only be deleted together with those MIB modules that depend on it by importing any MIB objects from it.
1.From the File menu, choose Delete MIB (or  from the main tool bar). A shuffle dialog will appear. It contains two lists of MIB modules. The left list shows all MIB modules available from the current MIB repository. The right list shows the MIB modules that are to be deleted.
from the main tool bar). A shuffle dialog will appear. It contains two lists of MIB modules. The left list shows all MIB modules available from the current MIB repository. The right list shows the MIB modules that are to be deleted.
2.Select any MIB modules you want to delete from the left list of available MIB modules. Click on the Add button to move the selected modules to the right list of MIB modules that should be deleted. Any MIB modules that depend on a MIB that is moved to the right list will be moved to the right list too. This ensures that MIB Explorer has always a consistent view on MIB data.
3.Select any MIB modules you want to preserve from deletion in the right list. Click on the Remove button to move the selected modules to the left list of available MIBs. Any MIB modules that preserved MIB module depends on will also preserved from deletion.
4.Click on the OK button to execute the changes made.
5.Confirm the deletion of the displayed number of MIB modules by choosing the Yes option.
MIBs can be exported from the current MIB repository to:
1.Plain text files
2.HTML files
3.XML files that are using the SMI DTD v0.1
4.XML Schema files (XSD)
5.PDF
To Export MIBs:
1.Choose Export MIBs from the File menu.
2.Choose the file format for the exported MIB modules.
3.Select the MIBs to export from the list of available modules and press the Add button to add them to the list of modules to be exported.
4.Choose the destination directory.
Any files that already exist in that directory might be overwritten!
5.Press OK to start the export operation. Each MIB module will be exported to a file, whose name will be the MIB modules name concatenated with one of the suffixes .txt, .html, .xml, .xsd or .pdf.
6.When exporting to PDF, you will be now prompted by an additional dialog for page layout and other document settings. You can choose the page size, footer, outline structure and font size. Press OK to export the selected MIBs with the selected settings.
With the MIB Explorer configuration file entry mibexplorer.compile.storeFilenameSeparator=- you can specify the hyphen character as separator, for example. Other characters or strings can be defined as separator as well, including the empty string.
The option Append the original file name separated by „_“ can be used to append the original file name of the MIB specification file the exported MIB module was imported from. The resulting file name will then be
<module-name><sep><orig-fname-w/o-suffix>.<suffix>
By default MIB Explorer will not record the file name of the imported MIB specification file in the compiled MIB modules. The original file name cannot be appended in that case. To let MIB Explorer record the file name, activate this option as described in section MIB Compiler.
In contrast to Compiling MIBs, Importing a MIB compiles a single MIB file and directly loads the contained MIB modules into the MIB tree.
To Import a MIB:
1.Choose Import MIB ( ) from the File menu.
) from the File menu.
2.Select the MIB file to import.
3.Press the Open button to compile the selected file, add it to the current MIB repository, and load the contained MIB modules. If there is a syntax error in the MIB file, then the MIB File Editor will open with that file and the cursor will be positioned at the error location in that file. None of the contained MIB modules will be loaded nor added to the MIB repository if the parser detects a syntax error.